 What is Tenant Screening in California and Why is it Important?
What is Tenant Screening in California and Why is it Important?
Tenant screening is an essential process for landlords and property managers in California to evaluate prospective tenants before signing a lease agreement. It involves collecting and analyzing various pieces of information about a tenant’s background, financial standing, and rental history to determine whether they are a suitable candidate for renting a property. This practice is crucial in ensuring that landlords make informed decisions while also protecting their investments.
In California, tenant screening is especially important due to the state’s highly competitive rental market, which can involve a mix of renters with varying financial situations, histories, and backgrounds. With the large number of applicants for rental properties, conducting thorough tenant screening can help landlords minimize risks and select tenants who are most likely to adhere to the lease agreement and pay rent on time.
The Significance of Tenant Screening in California
California’s rental market has unique characteristics, including high demand for housing, diverse tenant demographics, and a complex regulatory environment. Tenant screening in California helps landlords address various challenges, such as:
- Reducing the Risk of Non-Payment of Rent: By reviewing credit histories and income verification, landlords can assess whether applicants are financially capable of paying rent on time.
- Minimizing the Risk of Property Damage: Rental history checks can reveal whether a prospective tenant has a track record of damaging rental properties or violating lease terms.
- Ensuring Legal Compliance: Tenant screening allows landlords to adhere to legal standards by avoiding discriminatory practices and ensuring they follow California’s fair housing laws.
Ultimately, tenant screening is about managing risk, protecting property values, and fostering positive landlord-tenant relationships. By making informed decisions, landlords can reduce costly mistakes and avoid the complications of eviction or late rent payments.
Types of Background Checks in Tenant Screening in California
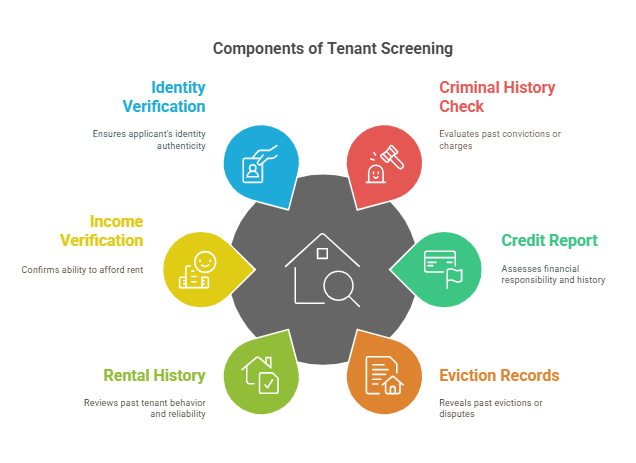
In California, tenant screening reports typically include several key components, which help landlords assess the qualifications and risks associated with a potential tenant:
- Criminal History Check: This checks for any past criminal convictions or ongoing charges against the applicant. While California law restricts the use of criminal records in tenant screening under certain circumstances (discussed later), landlords may still need to review an applicant’s criminal history to ensure the safety of the neighborhood and the property.
- Credit Report: A credit report provides insights into an applicant’s financial responsibility. This includes credit scores, outstanding debts, payment history, and any bankruptcy filings. A credit report is valuable for assessing whether a tenant is likely to pay rent on time and whether they have a history of financial mismanagement.
- Eviction Records: Eviction records can reveal whether the tenant has previously been evicted or had legal disputes with previous landlords. This is critical for understanding whether the applicant may have a pattern of behavior that could make them a risk for future evictions.
- Rental History: Past rental history helps landlords evaluate whether the applicant has been a reliable tenant in the past. This includes references from previous landlords, payment records, and adherence to lease terms. A strong rental history can demonstrate that the applicant is likely to fulfill their lease obligations.
- Income Verification: Landlords typically verify an applicant’s income to ensure that they can afford the rent. This can be done through pay stubs, bank statements, or tax returns. In California’s high-cost housing market, ensuring that tenants can pay rent is a crucial factor in tenant screening.
- Identity Verification: Identity verification ensures that the applicant is who they claim to be. This typically includes checks on the applicant’s Social Security number (SSN) or government-issued ID.
Why Tenant Screening is Essential for Landlords in California
Tenant screening is an indispensable tool for landlords and property managers to ensure the success of their rental operations. By conducting thorough screenings, landlords can achieve several benefits:
- Risk Reduction: The information provided in tenant screening reports helps landlords avoid tenants who may cause trouble, such as late payments, property damage, or legal issues.
- Legal Protection: By adhering to tenant screening regulations and avoiding discriminatory practices, landlords can minimize the risk of lawsuits and legal complications.
- Operational Efficiency: With a reliable tenant screening process in place, landlords can streamline the application process and choose tenants more quickly and confidently, improving the overall efficiency of their rental operations.
The Tenant Screening Process in California
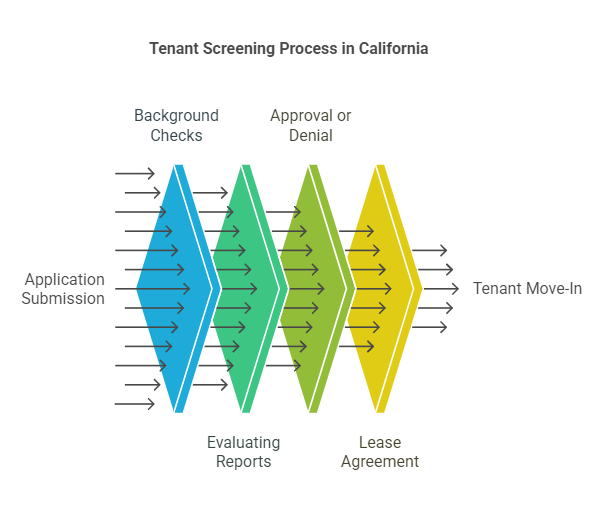
The tenant screening process generally involves several key steps, which help landlords assess the suitability of applicants:
- Application Submission: Prospective tenants complete a rental application form, which collects their personal information, rental history, employment details, and consent for background checks.
- Background Checks: Once the application is submitted, landlords use tenant screening services to pull background checks. This may include criminal checks, credit reports, eviction records, and rental histories.
- Evaluating Reports: After receiving the reports, landlords evaluate the information based on criteria set forth in their rental policies, such as a certain credit score threshold or no prior evictions.
- Approval or Denial: Based on the information gathered from the screening process, landlords decide whether to approve or deny the application. In some cases, the applicant may be asked for additional documentation or clarification before a decision is made.
- Lease Agreement: If the applicant is approved, a lease agreement is signed, and the tenant moves into the property.
While this process may seem straightforward, it is important for landlords to ensure that they comply with California laws throughout the screening process. For example, landlords must provide applicants with copies of any reports used in the screening process and give them an opportunity to dispute any inaccuracies in those reports.
In summary, tenant screening in California is a critical step for landlords to manage risk, ensure legal compliance, and maintain the overall quality of their rental properties. By understanding the types of background checks included in a screening report and following the process correctly, landlords can make more informed decisions and select tenants who will contribute to a positive rental experience.
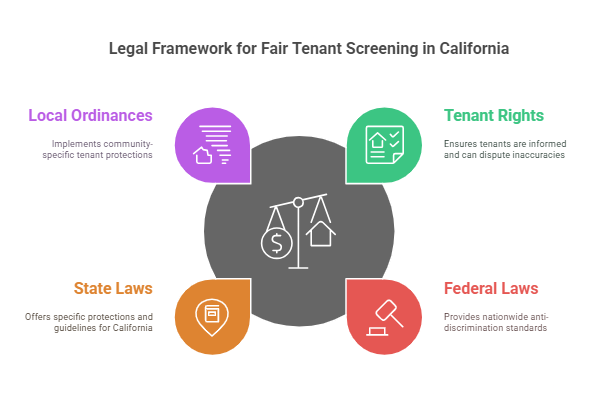
Legal Framework for Tenant Screening in California
Tenant screening is a crucial step for landlords to ensure they are renting to reliable tenants. However, in California, there are several legal frameworks that regulate how landlords can screen tenants to ensure fairness and compliance with state and federal laws. These regulations help protect both the landlord’s rights and the rights of tenants, promoting a rental process that is free from discrimination and bias. Below, we explore the most important laws and regulations that govern tenant screening in California.
Key Legal Regulations for Tenant Screening
- Fair Housing and Non-Discrimination Laws One of the most important aspects of tenant screening in California is ensuring compliance with fair housing laws. The California Fair Employment and Housing Act (FEHA) prohibits discrimination against tenants based on protected characteristics such as race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender, disability, and familial status. The federal Fair Housing Act (FHA) reinforces this by also protecting tenants from discrimination due to source of income, sexual orientation, or marital status.Landlords must adhere to these laws when screening tenants, ensuring that their criteria are applied uniformly to all applicants and that no one is unfairly excluded based on their race, gender, or other protected characteristics. To avoid legal issues, landlords should be careful to:
- Apply uniform screening criteria for all applicants.
- Avoid asking questions related to an applicant’s race, religion, family status, or any other protected category during the screening process.
- Ensure that policies on pet ownership, income requirements, and rental history are applied consistently.
- California Consumer Credit Reporting Agencies Act (CCRAA) The CCRAA regulates how credit reports can be used in tenant screenings in California. Before using a credit report, landlords must obtain written consent from the tenant applicant. The consent must be clear and explicit about the tenant’s rights, including the right to dispute the information on the report.If a landlord uses the credit report to deny an application, they are required to provide the tenant with an adverse action notice. This notice must explain why the tenant was rejected, detail the credit report or other information that led to the rejection, and inform the applicant of their right to request a copy of the report and challenge its accuracy.
- Ban the Box Legislation Under California’s Ban the Box law, landlords are prohibited from asking about criminal history on initial rental applications. This applies to most cities and counties in California and is designed to give applicants with criminal records a fair chance by evaluating their qualifications without bias. Criminal background checks can only be performed later in the process, after a conditional offer has been extended to the applicant.The Ban the Box law limits how landlords can use criminal history in decision-making. For example, a landlord must consider how the conviction relates to the rental situation and whether it occurred within a certain period. In general, landlords are discouraged from automatically disqualifying applicants based solely on past criminal activity.
- Eviction History Restrictions California has specific rules regarding the use of eviction records in tenant screening. As a general rule, eviction records that are older than 7 years cannot be used to deny a tenant application. Moreover, landlords cannot automatically reject applicants simply because they have been evicted. Instead, they must consider the circumstances surrounding the eviction and how it relates to the applicant’s suitability as a tenant.Local ordinances in California cities may have even more restrictive rules regarding eviction records. For example, San Francisco and Los Angeles have additional protections in place to limit how eviction histories are used, and some cities do not allow landlords to use eviction records at all unless there are substantial grounds for concern. Landlords should be aware of these local regulations to ensure compliance.
- Rent Control Ordinances Several cities in California, including Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Oakland, have rent control laws that impose restrictions on how landlords can rent to tenants. These local laws may affect how landlords can evaluate potential tenants. Rent control laws also often place limits on rent increases and require landlords to justify eviction decisions based on specific criteria.In cities with rent control ordinances, landlords must ensure that their tenant screening processes do not violate local rent control laws. This includes understanding which screening criteria are allowable, including income verification, criminal background checks, and eviction history. Rent control laws often require landlords to provide tenants with more rights to challenge eviction decisions or rent increases.
Best Practices for Tenant Screening in California
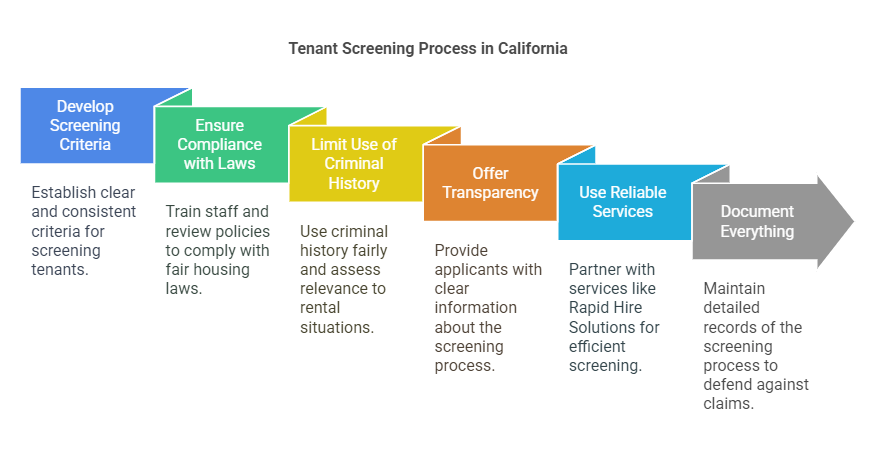
Conducting tenant screenings in California requires careful attention to legal obligations as well as best practices that ensure fairness, transparency, and accuracy. Below are some best practices that landlords can follow to protect themselves from legal issues and ensure they are screening tenants properly.
- Develop and Communicate Clear Screening Criteria Landlords should have clear, written criteria for tenant screening that includes specific requirements for credit history, rental history, income verification, and criminal background. These criteria should be consistent for all applicants to avoid any appearance of discrimination.Clear screening criteria help ensure that all applicants are evaluated on the same basis and provide landlords with a defense in case of a fair housing lawsuit. Additionally, landlords should make sure to communicate their screening criteria clearly to all applicants to set expectations and avoid misunderstandings.
- Ensure Compliance with Fair Housing Laws Landlords must be aware of both state and federal fair housing laws and take proactive steps to ensure compliance. This includes:
- Training staff on how to avoid discriminatory behavior during the screening process.
- Regularly reviewing policies and practices to ensure they don’t unintentionally violate the Fair Housing Act or state law.
- Maintaining documentation to demonstrate that screening decisions are based on legitimate factors, such as income and rental history, rather than on discriminatory practices.
- Limit Use of Criminal History As per the Ban the Box law and other regulations, landlords must ensure they use criminal history in a way that does not unfairly disadvantage applicants. Specifically:
- Criminal history should not be the primary deciding factor in rental applications.
- If criminal history is considered, landlords should assess whether the offense is relevant to the rental situation and whether it occurred within a reasonable time frame.
- Landlords should also be cautious about using arrest records or convictions that are unrelated to rental behavior.
- Offer Transparency in the Screening Process California law requires landlords to provide transparency during the tenant screening process. This includes giving applicants:
- Written notice of the screening process.
- Information about how their credit report, criminal history, or eviction record will be used.
- The right to dispute any inaccurate information on their tenant screening report.
Providing transparency ensures tenants know their rights and helps build trust in the rental process.
- Use a Reliable Tenant Screening Service To make the tenant screening process more efficient and legally compliant, landlords can use services like Rapid Hire Solutions. These services help landlords screen tenants in a way that complies with California laws. Rapid Hire Solutions provides comprehensive background checks, including criminal records, eviction history, credit reports, and income verification, ensuring that landlords can make informed decisions while adhering to legal guidelines.By partnering with Rapid Hire Solutions, landlords can streamline the process, reduce risk, and ensure they are using reliable, legally compliant screening practices.
- Document Everything Documentation is critical in defending against potential claims of discrimination. Landlords should keep detailed records of the entire tenant screening process, including:
- The application form.
- Any communications with the applicant.
- The screening report and the basis for any decision made.
- Any notices sent to the applicant, such as adverse action notices.
Proper documentation can protect landlords from legal challenges and ensure they are compliant with California’s tenant screening laws.
Tenant screening in California involves navigating a complex landscape of state and local laws designed to protect tenants from discrimination while allowing landlords to evaluate potential tenants effectively. By adhering to best practices and staying informed of the legal requirements, landlords can ensure they are making fair, legal, and informed decisions when selecting tenants. Services like Rapid Hire Solutions can be invaluable in helping landlords streamline the screening process, reduce risk, and maintain compliance with California’s ever-evolving tenant protection laws.
Legal Aspects of Tenant Screening in California
Tenant screening in California is not only essential for landlords but also heavily regulated to ensure fairness and prevent discrimination. The laws governing tenant screening are designed to protect tenants from bias and ensure that landlords make informed decisions based on legitimate criteria. In this section, we will dive deeper into some of the critical legal considerations that every landlord should be aware of when conducting tenant screenings in California.
Tenant Rights in California Regarding Tenant Screening
California tenants have specific rights when it comes to tenant screening. These rights are protected by both federal and state laws, and landlords must ensure they do not violate these rights during the screening process. Below are some important tenant rights:
- Right to Know When a Screening is Conducted Under California law, tenants have the right to know when a screening report is being conducted. Landlords must obtain the tenant’s written consent before obtaining a credit report or criminal background check. If a screening decision is made based on the tenant’s background, the landlord must provide an adverse action notice informing the tenant of the decision and the reason for it.
- Right to Review and Dispute the Screening Report Tenants have the right to request a copy of the screening report used by the landlord to make a rental decision. If a tenant believes the information is inaccurate or incomplete, they have the right to dispute the data. The landlord is required to provide the tenant with an explanation of how they used the screening report in their decision-making process and allow the tenant to challenge the findings.
- Limitations on Discrimination As part of the California Fair Employment and Housing Act (FEHA) and the Fair Housing Act (FHA), tenants are protected from discrimination based on their race, religion, sex, gender, familial status, disability, sexual orientation, and more. Landlords are prohibited from using certain criteria, such as criminal history, in ways that disproportionately affect certain groups of applicants unless there is a valid, relevant reason for doing so.
- Right to Privacy While landlords are allowed to gather information during the tenant screening process, tenants also have the right to privacy regarding their personal data. This means that landlords must take steps to ensure that any personal information, including background checks and credit reports, is handled confidentially and is not shared without the tenant’s consent.
Local Ordinances and Laws Impacting Tenant Screening
In addition to state and federal laws, many cities and counties in California have enacted local ordinances that may impose stricter rules for tenant screening. These ordinances are designed to provide additional protection to tenants and regulate the use of eviction history, criminal background, and other factors in the screening process. Here are some examples:
- San Francisco San Francisco has robust tenant protections, including ordinances that limit the use of eviction history in rental decisions. Landlords in San Francisco are prohibited from using eviction history that is over 7 years old to reject tenants. Additionally, landlords cannot use criminal history unless they can demonstrate a direct connection to the safety or security of the rental property.
- Los Angeles Los Angeles also has tenant protections that restrict the use of eviction records. The city has passed laws making it more difficult for landlords to use eviction records against tenants, especially for evictions that are older than 7 years. The city has also passed legislation requiring landlords to consider the reasons for eviction, such as whether it was for failure to pay rent or a situation beyond the tenant’s control.
- Oakland Oakland has unique rules regarding tenant screening, including restrictions on asking about criminal history. The city also has laws prohibiting discrimination against tenants based on source of income. Landlords in Oakland are required to be transparent about the criteria they use when selecting tenants, and they must offer opportunities for applicants to dispute screening decisions.
It is essential for landlords to be aware of the local ordinances in their area and ensure they comply with any additional tenant protections that may apply. Failure to follow these rules can lead to legal challenges and penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What can be included in a tenant screening report in California?
A tenant screening report in California typically includes a variety of information to help landlords evaluate an applicant’s suitability. This may include:
- Credit report: This provides insight into the applicant's financial responsibility and creditworthiness.
- Criminal background check: A review of the applicant’s criminal history to assess any potential risks related to the rental property.
- Eviction history: A record of any past evictions filed against the applicant, which can indicate past rental issues.
- Rental history: Information about the applicant's past tenancies, including whether they paid rent on time and maintained the property.
Can a landlord refuse to rent to someone with a criminal record in California?
Under California's Ban the Box law, landlords are prohibited from asking about criminal history on rental applications. Criminal background checks can only be conducted after a conditional offer has been extended. However, while landlords cannot automatically deny an applicant based solely on criminal history, they may consider it if it is relevant to the rental situation (e.g., if the crime is violent or involves property damage).
How long do eviction records stay on a tenant’s record in California?
Eviction records typically remain on a tenant’s record for 7 years in California. However, certain local ordinances may reduce this time frame or impose additional restrictions on how eviction records can be used in screening decisions. After the 7-year mark, eviction records generally cannot be considered by landlords when evaluating new applicants.
What are the Fair Housing Act guidelines regarding tenant screening in California?
The Fair Housing Act (FHA) prohibits landlords from discriminating against tenants based on protected characteristics such as race, gender, disability, familial status, and national origin. Landlords must apply their screening criteria consistently to all applicants and ensure that decisions are based on objective, non-discriminatory factors. For example, a landlord cannot automatically reject an applicant because of their ethnicity or family situation.
Can a tenant dispute the results of a screening report?
Yes, tenants in California have the right to dispute any inaccuracies in their screening report. If a tenant believes that the information provided in a credit report, criminal background check, or eviction history is incorrect, they can challenge it by contacting the reporting agency and providing evidence to support their case. Tenants are also entitled to a copy of the report and must be informed if the information was used to deny their application.
Conclusion
Tenant screening in California is a complex process that requires landlords to carefully navigate a web of legal regulations and guidelines. By understanding the legal aspects of tenant screening, ensuring compliance with fair housing laws, and adopting best practices for screening applicants, landlords can protect themselves from legal issues and ensure that they make informed, unbiased decisions.
Moreover, working with a reliable tenant screening service like Rapid Hire Solutions can help landlords ensure they are meeting all legal requirements and providing a transparent, non-discriminatory screening process. Whether you are a first-time landlord or an experienced property manager, staying informed about the laws and best practices surrounding tenant screening is essential for creating a fair and compliant rental process.
By keeping up-to-date with local ordinances and understanding tenant rights, landlords can not only reduce risks but also build a positive reputation as responsible property managers who respect tenants’ rights. This is a key factor in maintaining a profitable and successful rental business in California.
