What is Identity Verification?

Understanding Identity Verification and Its Importance
Identity verification is the process of confirming that a person is who they claim to be. It plays a critical role in many sectors, especially in preventing fraud, ensuring security, and protecting personal data. In today’s digital age, where transactions and services are increasingly conducted online, identity verification has become an essential part of maintaining trust and safety.
Why Identity Verification Matters
Identity verification is used to ensure that the person requesting access to a service, account, or transaction is legitimate. Whether it’s logging into an online bank account, signing up for a new email, or applying for a job, the verification process is designed to keep unauthorized individuals from gaining access. It helps reduce fraud, identity theft, and other illegal activities that might arise from improper or unsecured use of personal data.
Common Methods of Identity Verification
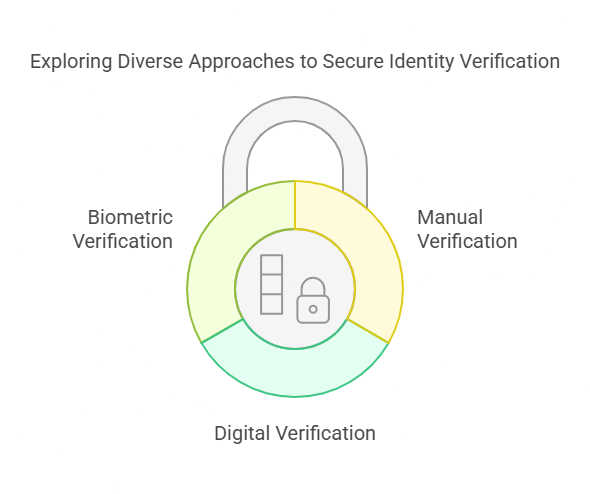
There are different methods used for verifying identities, depending on the context and security requirements. Some of the common methods include:
- Manual Verification: This traditional method involves verifying personal information such as government-issued ID cards, proof of address, or employment details through human review. While reliable, it can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
- Digital Verification: Involves the use of online platforms and services to validate a person’s identity using data like email addresses, phone numbers, or government databases. Digital verification is faster and more efficient but requires a high level of data security.
- Biometric Verification: This method uses unique physical traits like fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice patterns to authenticate a person’s identity. Biometric verification is often considered the most secure and hard to falsify.
Industries That Rely on Identity Verification
Certain industries rely heavily on secure identity verification systems. These include:
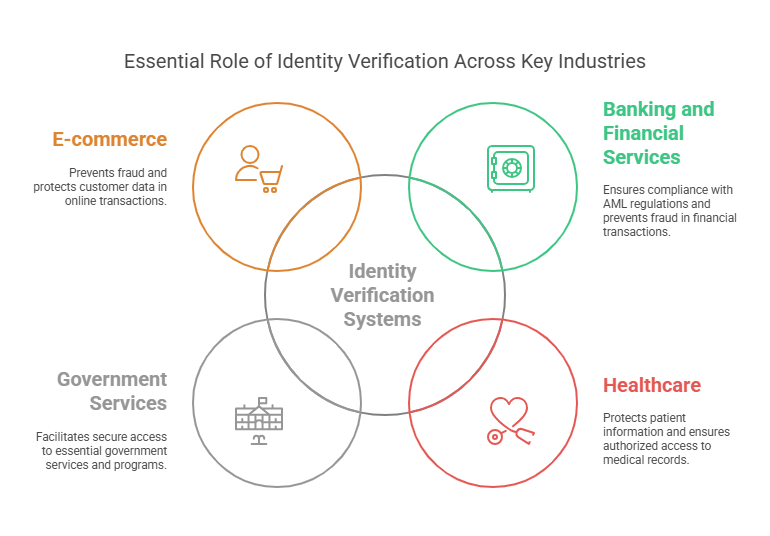
- Banking and Financial Services: To comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and prevent fraud, financial institutions require identity verification for opening accounts, conducting high-value transactions, and applying for loans.
- Healthcare: To protect patient information and comply with regulations like HIPAA, healthcare providers use identity verification to ensure that medical records and prescription information are accessed only by authorized individuals.
- Government Services: Governments use identity verification to provide access to services such as tax filing, passport issuance, and welfare programs.
- E-commerce: Online retailers often implement identity verification to prevent fraudulent transactions, protect customer data, and verify payment methods.
How Identity Verification Helps Prevent Fraud and Identity Theft
By confirming that individuals are who they claim to be, identity verification acts as a safeguard against fraud and identity theft. It ensures that criminals cannot impersonate others to gain access to sensitive information or financial assets. Additionally, it prevents individuals from using stolen identities to commit crimes such as financial fraud or unauthorized access to confidential records.
How Does Identity Verification Work?
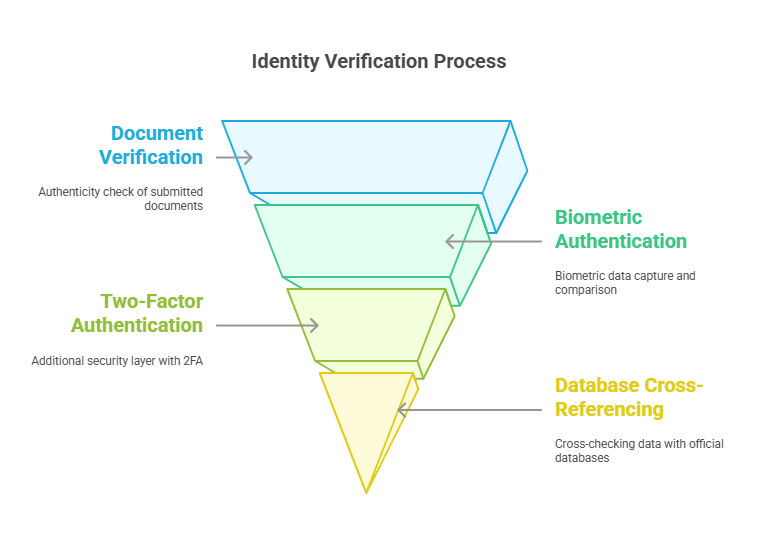
The Steps Involved in the Identity Verification Process
The process of identity verification varies depending on the method and industry, but typically follows a series of steps to ensure accuracy and security. Here’s a general breakdown of how identity verification works:
- Submission of Personal Information
The first step in the identity verification process involves submitting personal details. This could include uploading a government-issued ID, a selfie, a utility bill, or other proof of identity. The user is often asked to provide their name, date of birth, address, and other identifying information. - Document Verification
In cases where documents are submitted, the next step involves verifying their authenticity. Document verification software or tools analyze the documents to ensure they are legitimate, valid, and not altered. These tools scan for security features like watermarks, barcodes, and holograms to confirm the document’s authenticity. - Biometric Authentication (if applicable)
If biometric verification is used, the next step may involve capturing a user’s fingerprint, facial scan, or voice sample. Biometric data is then compared to databases or pre-recorded data to confirm identity. - Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
To enhance security, many identity verification processes include two-factor authentication (2FA). This requires the user to verify their identity by entering a code sent to their phone, email, or a dedicated authenticator app. This additional layer of verification ensures that the user requesting access is legitimate. - Database Cross-Referencing
For digital verification, data provided by the individual may be cross-checked against government or industry-specific databases to confirm accuracy. For example, financial institutions may check identity information against credit bureaus, while healthcare services might cross-reference data with national health databases. - Completion of the Verification Process
Once all the necessary steps are completed, the system will notify the individual or organization if the verification is successful. If the process is unsuccessful, users are usually informed and provided with steps on how to resolve the issue.
Tools and Technologies Used in Identity Verification
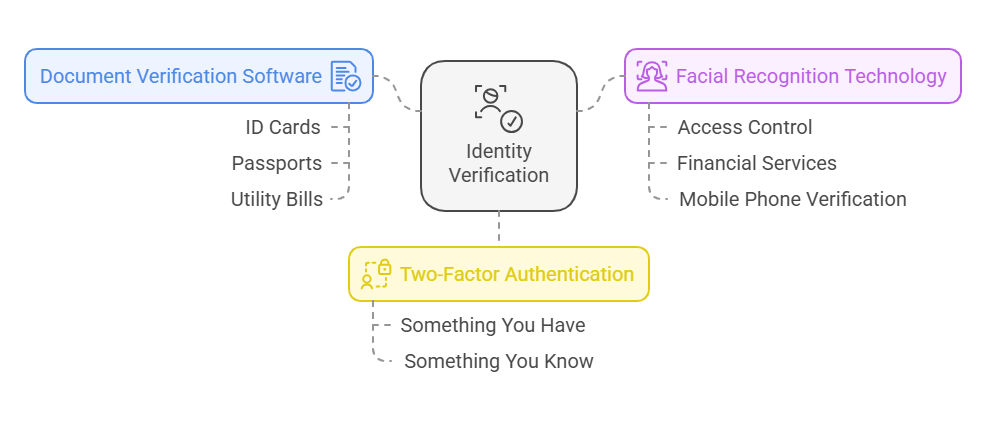
To carry out identity verification effectively and securely, several tools and technologies are commonly used. Here are a few of the most prominent:
- Document Verification Software: This software analyzes various features of submitted documents, such as ID cards, passports, and utility bills, ensuring they are valid and free from tampering. It helps verify the authenticity of physical documents in a matter of seconds, reducing manual error.
- Facial Recognition Technology: This is a biometric authentication method where a person’s face is scanned and compared to stored facial features in a database. This technology is widely used for access control, financial services, and mobile phone verification.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): As mentioned earlier, this is a common method of providing a second layer of security by requiring users to authenticate their identity through something they have (a phone or an app) and something they know (password or PIN).
Sample Identity Verification Process Flow
Here’s an example of a typical identity verification process flow:
- Step 1: The user is prompted to submit basic information (name, address, date of birth, etc.) on a secure platform or via a mobile app.
- Step 2: The user uploads a scanned copy or photo of their government-issued ID.
- Step 3: The document is verified through software to confirm authenticity.
- Step 4: If necessary, the user is asked to perform biometric verification (e.g., face scan or fingerprint scan).
- Step 5: The user receives a code on their phone or email, which they must enter to complete the process.
- Step 6: The system cross-references the submitted data against relevant databases.
- Step 7: Once confirmed, the user is granted access or informed of the results.
How Rapid Hire Solutions Assists with Identity Verification
Rapid Hire Solutions provides businesses with seamless identity verification services, especially in the context of employment screening and recruitment. They help employers streamline the process by ensuring that candidates’ identities are thoroughly validated before being hired. Through their services, companies can efficiently verify the identity of job applicants, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring a secure and compliant hiring process.
Tips for Ensuring a Smooth and Secure Verification Process
For both individuals and organizations, the identity verification process should be as smooth and secure as possible. Here are some tips to ensure success:
- Use Secure Platforms: Always choose reputable and secure platforms for submitting personal information.
- Double-Check Documents: Make sure that the documents submitted are clear and legible to avoid delays in the verification process.
- Be Aware of Phishing Scams: Be cautious of phishing attempts and never share sensitive information through untrusted channels.
- Keep Personal Information Updated: Ensure that your personal information is up-to-date, including your address and other essential details.
Legal Aspects of Identity Verification
Identity verification is not only a practical necessity for many industries but also a legally regulated process, especially in sectors that deal with sensitive or personal data. Here are some key legal aspects surrounding identity verification:
- Privacy Laws and Data Protection
One of the most important legal considerations in identity verification is data protection. Organizations must comply with privacy laws that govern the collection, storage, and sharing of personal data. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States place stringent requirements on how businesses manage user data during identity verification processes. - Compliance with Industry Regulations
Various industries have specific regulations regarding identity verification. For example, financial institutions are required to verify identities to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, while healthcare providers must ensure that patient information is protected and correctly verified under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). - Security and Confidentiality
Employers and service providers must ensure that the data collected during the identity verification process is handled securely. This means using encryption, secure storage solutions, and ensuring that access to sensitive information is restricted. Failure to follow these security protocols can result in severe legal consequences, including lawsuits and regulatory fines. - Retention and Deletion of Data
Another important legal consideration is how long identity verification data is retained. Many laws require businesses to only store verification data for as long as it is necessary for the purpose it was collected. Once the data is no longer needed, it must be securely deleted to avoid unauthorized access or potential misuse.
FAQs About Identity Verification
Why is identity verification important for businesses?
Identity verification is crucial for businesses to prevent fraud, ensure the legitimacy of their customers or employees, and comply with industry regulations. It helps establish trust and security, which are essential for maintaining customer relationships and business operations.
How do businesses ensure that identity verification processes are secure?
Businesses use various tools and technologies such as encryption, biometric data, and secure document verification systems. They also comply with legal requirements and industry best practices to ensure that identity verification is performed securely and protects user data.
What documents are typically required for identity verification?
The documents required for identity verification can vary depending on the industry and the service being provided. Common documents include government-issued identification cards (e.g., driver’s licenses, passports), utility bills, social security numbers, or biometric data such as fingerprints or facial scans.
Is biometric data a safe form of identity verification?
Yes, biometric data, such as facial recognition or fingerprints, is considered one of the most secure forms of identity verification. However, the safety of biometric data depends on how it is stored and protected. Organizations must use secure systems and encryption to protect this sensitive data.
How does identity verification prevent fraud?
Identity verification helps prevent fraud by ensuring that the person who claims an identity is indeed who they say they are. By verifying documents, using biometric checks, and cross-referencing data with trusted databases, businesses can reduce the risk of impersonation, identity theft, and other fraudulent activities.
Conclusion
Identity verification is a crucial process in the modern digital world. It is integral to protecting individuals and businesses from fraud, identity theft, and financial crimes. Whether in the context of employment, financial transactions, or government services, identity verification ensures that only legitimate individuals gain access to services and resources.
Understanding the various methods of identity verification, the technologies used, and the legal aspects that surround the process is essential for anyone involved in verifying identities. Businesses must comply with data protection laws and ensure that their verification processes are secure, efficient, and legally compliant. Additionally, with the rise of digital and biometric verification, it’s important for both organizations and individuals to stay informed about the best practices for protecting personal data.
By following secure verification methods and being mindful of legal and privacy requirements, both individuals and businesses can contribute to a safer and more trustworthy environment for all.
