 What is Risk Mitigation in Cybersecurity and Why is It Crucial?
What is Risk Mitigation in Cybersecurity and Why is It Crucial?
Risk mitigation in cybersecurity refers to the process of identifying, evaluating, and reducing the potential impact of cyber threats and vulnerabilities that could harm an organization’s digital infrastructure, assets, and reputation. In today’s increasingly digital world, the need for robust risk mitigation strategies has never been more critical. Cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity—it is a core business requirement, as cyberattacks can cause severe financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
Cyber risk mitigation involves understanding the variety of cyber threats organizations face and implementing strategies to reduce their exposure to these threats. It’s about minimizing the likelihood of a breach or attack, as well as reducing the severity of its consequences if it occurs. The key goal is to prevent incidents before they happen, detect potential threats early, and respond swiftly to minimize damage.
Understanding Cyber Risks
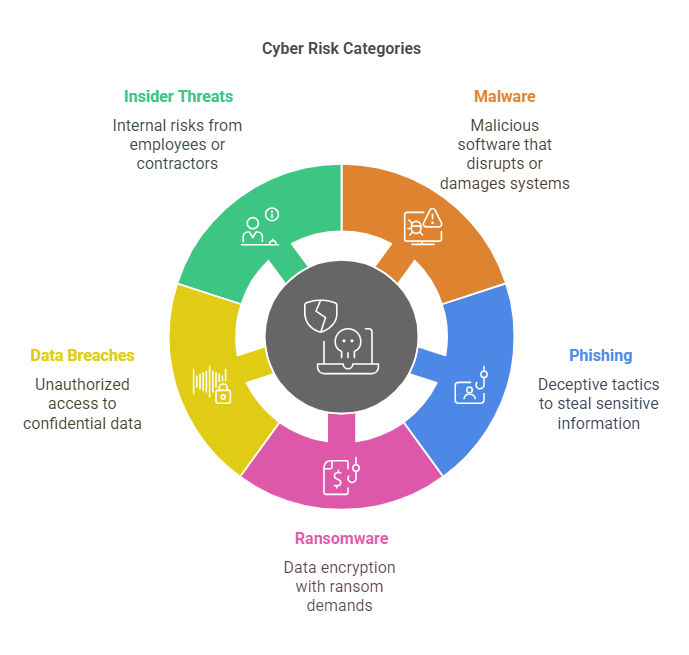
Organizations today face a wide range of cyber threats. These threats evolve rapidly, and what was considered secure just a few years ago may no longer be sufficient to protect against the sophisticated tactics employed by cybercriminals. Below are some of the most common types of cyber risks that organizations must be prepared to mitigate:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt or damage computer systems. Malware includes viruses, worms, and spyware, which can infiltrate an organization’s network, corrupt data, and harm devices.
- Phishing: A form of social engineering where attackers trick individuals into providing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or financial details, by pretending to be a trusted entity.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data, demanding a ransom for its release. Organizations can face significant downtime and financial losses due to ransomware attacks.
- Data Breaches: The unauthorized access or disclosure of confidential data, such as personal information, customer records, or proprietary business data. Data breaches can lead to severe reputational damage and legal consequences.
- Insider Threats: Cyber threats that originate from within the organization, often from disgruntled employees or contractors who have access to sensitive systems and data.
The Importance of Proactive Risk Mitigation
A proactive approach to risk mitigation is essential in preventing cyber threats from disrupting an organization’s operations. Regular updates to software and systems, continuous monitoring, and ongoing employee training can help reduce vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit.
Organizations should avoid being reactive and only responding to cyberattacks once they occur. By that point, the damage may already be done. Instead, organizations must focus on prevention, ensuring that their systems and infrastructure are constantly updated with the latest security patches and that employees are educated on identifying potential threats such as phishing attempts.
Cyber risk mitigation also involves having the right technology and processes in place to respond effectively when an incident occurs. This includes having robust backup systems, incident response protocols, and a well-defined recovery strategy. The faster an organization can identify and respond to a cyber incident, the less damage it will suffer.
Key Elements of Risk Mitigation in Cybersecurity
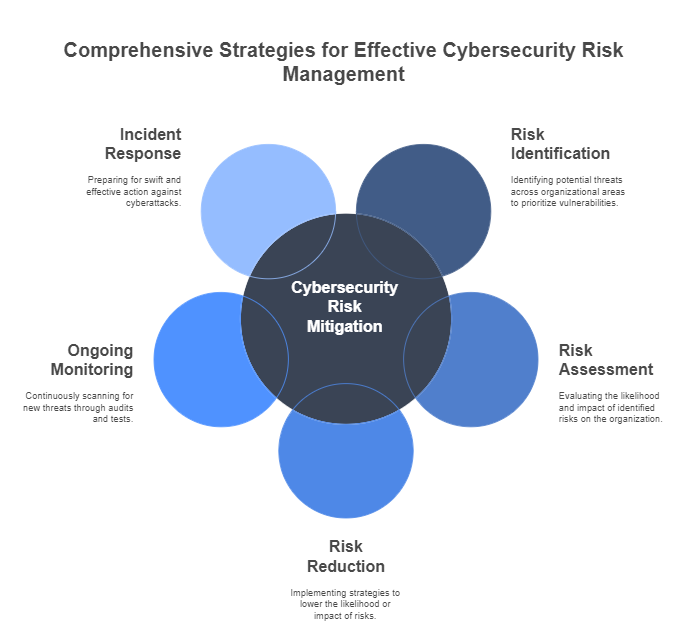
Risk mitigation in cybersecurity revolves around a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and reducing risks. The following steps are key components of a successful cybersecurity risk mitigation strategy:
- Risk Identification: The first step in mitigating cyber risks is to identify potential threats. This involves looking at various areas of the organization, including network infrastructure, software applications, data storage, and human factors. By understanding where vulnerabilities exist, organizations can prioritize their efforts to address the most pressing threats.
- Risk Assessment: Once threats are identified, the next step is to assess their potential impact. This involves evaluating the likelihood of each risk occurring and determining the potential consequences for the organization. For example, an organization may assess the likelihood of a data breach and the potential damage it could cause in terms of financial loss, legal penalties, and customer trust.
- Risk Reduction: After assessing the risks, organizations need to implement strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of these risks. This can be done through various measures, such as updating software, implementing firewalls, training employees, and using encryption to protect sensitive data.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, so ongoing monitoring is essential for identifying new risks as they emerge. Regular audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability scans can help identify weaknesses before cybercriminals can exploit them.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Even with the best mitigation strategies in place, no system is completely immune to cyber threats. Having a well-defined incident response plan and recovery strategy is critical in ensuring the organization can respond swiftly and effectively to a cyberattack.
The Role of Employee Training in Risk Mitigation
One often overlooked aspect of risk mitigation is the role of employees in maintaining cybersecurity. Human error is one of the leading causes of cyber incidents. Whether it’s falling for a phishing email, using weak passwords, or inadvertently exposing sensitive data, employees can unintentionally open the door to cybercriminals.
Organizations must provide comprehensive cybersecurity training for all employees. Training should cover:
- How to identify phishing and social engineering attacks.
- Best practices for creating strong, secure passwords.
- The importance of keeping software up to date.
- How to protect personal and sensitive data.
- What to do in the event of a potential cyber incident.
In addition to training, organizations can implement policies that promote good cybersecurity hygiene, such as requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA), restricting access to sensitive information based on job roles, and regularly auditing employee activity to ensure compliance with cybersecurity protocols.
The Importance of a Cybersecurity Framework
Implementing a cybersecurity framework is one of the most effective ways to guide risk mitigation efforts. Cybersecurity frameworks provide organizations with a set of guidelines, best practices, and standards to follow, ensuring that they address all aspects of cybersecurity risk management.
Some well-known cybersecurity frameworks include:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF): Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework is widely used in the U.S. and provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks.
- ISO/IEC 27001: A globally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS), ISO 27001 helps organizations ensure that their cybersecurity practices align with international best practices.
- CIS Controls: The Center for Internet Security (CIS) offers a set of 20 critical security controls that organizations can use to mitigate the most common cybersecurity risks.
By adopting these frameworks, organizations can improve their risk mitigation strategies, ensuring they follow industry best practices and stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
Effective Risk Mitigation Strategies in Cybersecurity: Best Practices and Tools
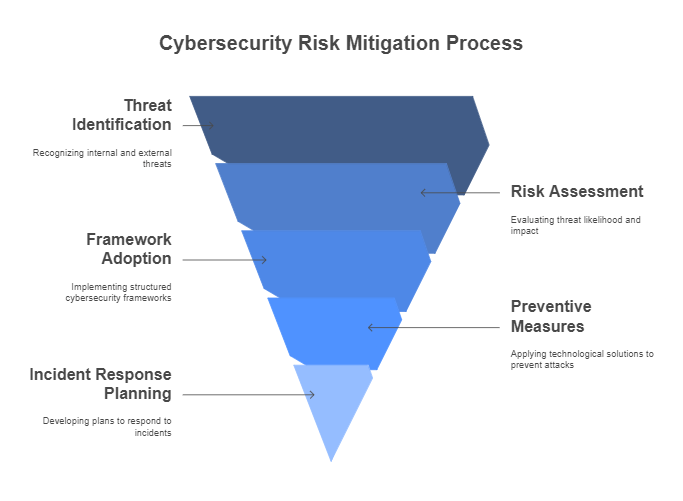
In the face of ever-evolving cyber threats, risk mitigation strategies are essential for ensuring the safety and security of an organization’s data, assets, and reputation. These strategies are crucial in minimizing the impact of potential cyberattacks and breaches. In this section, we will explore several effective risk mitigation strategies and the best practices organizations can implement to protect themselves from cyber threats. By understanding these strategies, businesses can adopt more proactive, comprehensive measures to safeguard their critical digital infrastructure.
1. Threat Identification: Understanding Potential Cyber Threats
The first step in any cybersecurity risk mitigation strategy is threat identification. To protect against cyber risks, an organization must first understand the types of cyber threats that could potentially harm its infrastructure. Threat identification involves recognizing both internal and external threats that could exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s network and systems.
Some key activities involved in threat identification include:
- Conducting Regular Risk Assessments: Regular risk assessments help organizations identify potential vulnerabilities in their network, systems, and applications. These assessments may include vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, where experts attempt to exploit weaknesses in a system to identify risks.
- Monitoring Threat Intelligence Feeds: Cybersecurity threat intelligence services provide up-to-date information about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By continuously monitoring these feeds, organizations can quickly identify new risks, such as zero-day vulnerabilities or evolving cyberattack techniques.
- Employee Reports and Feedback: Employees are often the first line of defense in identifying cyber threats. They can report suspicious activities or potential security concerns, such as phishing emails or unusual system behavior. Therefore, it is essential to establish clear reporting channels within the organization.
Organizations can use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to aggregate data from various sources, including network devices, security applications, and employee reports, to detect suspicious activities and track patterns indicative of cyber threats.
2. Risk Assessment: Evaluating Likelihood and Impact
Once threats are identified, the next step is risk assessment. Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of a cyberattack on the organization. Understanding which threats pose the greatest risk allows an organization to prioritize its cybersecurity resources effectively.
The key elements of a risk assessment include:
- Likelihood Evaluation: This involves determining how likely it is that a specific threat will exploit a vulnerability. The likelihood of an attack can be influenced by factors such as the organization’s industry, the current cybersecurity posture, and historical data on similar incidents.
- Impact Assessment: The potential impact of a cyberattack varies depending on the type of threat and the organization’s exposure. An attack on a customer database, for example, may have a greater impact than a breach of non-sensitive internal data. The assessment should consider both the financial and reputational damage caused by a breach.
- Risk Probability Matrix: Organizations can use a risk probability matrix to classify threats based on the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of their impact. This helps to focus efforts on the most critical vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation actions.
- Risk Mitigation Cost-Benefit Analysis: A risk assessment also involves weighing the cost of mitigating a risk against the potential impact of that risk. For instance, implementing encryption for sensitive data may incur significant costs, but the potential loss from a data breach could be far higher. This analysis helps determine whether to accept, avoid, or mitigate specific risks.
By conducting comprehensive risk assessments, organizations can understand where to focus their attention and resources to reduce the most critical cybersecurity threats.
3. Cybersecurity Frameworks: Structured Risk Mitigation Approaches
One of the most effective ways to manage cybersecurity risks is to adopt a recognized cybersecurity framework. These frameworks provide structured guidance and best practices to help organizations identify and mitigate cyber risks systematically. Below are a few widely recognized cybersecurity frameworks that businesses can implement to reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats:
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF)
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a comprehensive guide for managing cybersecurity risks. It consists of five core functions:
- Identify: Understand the organization’s cybersecurity risks, including assets, data, and vulnerabilities.
- Protect: Implement protective measures to limit or contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event.
- Detect: Continuously monitor systems for potential cybersecurity threats.
- Respond: Develop and implement response plans to mitigate the impact of cybersecurity incidents.
- Recover: Ensure that recovery processes are in place to restore normal operations after an incident.
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This framework helps organizations establish, implement, and maintain a comprehensive cybersecurity risk management system. By adopting ISO 27001, organizations ensure that their cybersecurity practices comply with globally recognized standards.
CIS Controls
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) offers a set of 20 critical security controls designed to address the most common cybersecurity risks. These controls range from establishing security baselines for hardware and software to implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and securing communication channels. The CIS Controls provide a practical, prioritized approach to improving an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
By adopting these frameworks, organizations can ensure that they follow industry-standard practices for identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber risks effectively.
4. Preventive Measures: Technological Solutions for Cybersecurity
Once potential risks and vulnerabilities are identified, organizations must implement preventive measures to safeguard their networks and systems. These technological solutions are critical in reducing the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls and IDS are foundational technologies that protect an organization’s network from unauthorized access. Firewalls act as barriers between internal systems and external networks, while IDS monitor network traffic for suspicious behavior that may indicate a breach.
Encryption
Encryption is a vital tool for protecting sensitive data. By encrypting data, organizations ensure that even if data is intercepted during transmission, it cannot be read without the decryption key. Strong encryption protocols are essential for protecting sensitive information such as customer records, payment information, and intellectual property.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective ways to secure user accounts and systems. MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors—something they know (password), something they have (phone or token), or something they are (biometric data). MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access, especially in the case of stolen credentials.
Regular Software Updates and Patching
Keeping software up to date is a critical preventive measure. Many cyberattacks exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Regularly applying patches and updates ensures that known vulnerabilities are addressed, reducing the likelihood of exploitation.
5. Incident Response Planning: Minimizing the Impact of Cyber Incidents
Even with the best preventive measures in place, no organization is immune to cyber threats. Therefore, having a comprehensive incident response plan (IRP) is essential to minimize the impact of cyber incidents. An IRP outlines the steps to take when a security breach or cyberattack occurs, ensuring that the organization responds promptly and efficiently to contain and mitigate the damage.
An effective incident response plan includes:
- Incident Detection and Reporting: Implement monitoring tools to detect unusual activity and establish a reporting protocol for employees to report suspicious incidents.
- Containment and Mitigation: Once an incident is identified, it is crucial to contain the threat to prevent further damage. This may involve isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or shutting down compromised accounts.
- Investigation and Root Cause Analysis: After the incident is contained, conduct a thorough investigation to understand how the breach occurred and identify the root cause. This will inform future risk mitigation efforts.
- Recovery and Restoration: The final step is restoring normal operations, recovering data from backups, and ensuring systems are secure before bringing them back online.
Rapid Hire Solutions: Supporting Risk Mitigation in Cybersecurity
Organizations like Rapid Hire Solutions can play a critical role in assisting businesses with implementing cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies. Rapid Hire Solutions offers cybersecurity services and tools designed to protect sensitive data and secure networks. By providing resources for risk assessments, threat identification, and cybersecurity frameworks, Rapid Hire Solutions helps businesses mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats and ensure their networks and systems are protected.
Legal Aspects: Understanding the Legal Implications of Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation
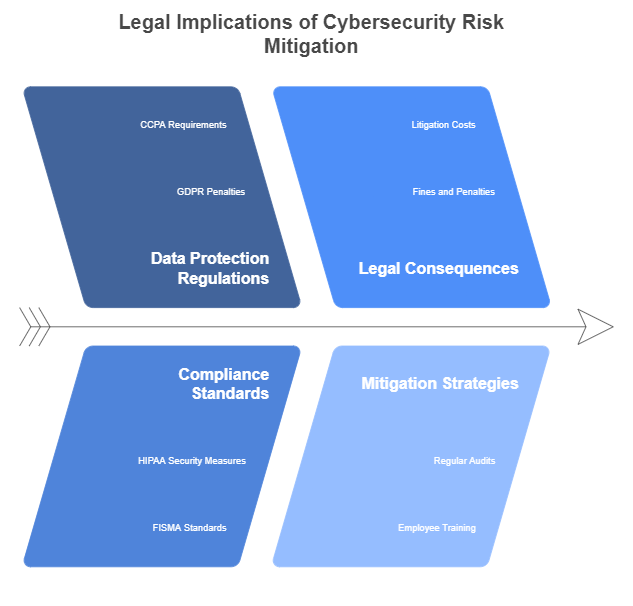
As organizations implement cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies, it is essential to recognize the legal aspects surrounding data protection, privacy, and compliance. The legal landscape for cybersecurity is evolving rapidly, and businesses must ensure they comply with various laws and regulations to avoid potential legal consequences.
1. Data Protection Regulations
Several data protection regulations are designed to safeguard personal and sensitive information. These laws require businesses to implement appropriate security measures to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to personal data.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enforced across the European Union (EU), the GDPR is one of the most comprehensive data protection regulations. It mandates that businesses implement strong cybersecurity measures to protect EU citizens’ personal data. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, including fines of up to 4% of global annual turnover or €20 million (whichever is higher).
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA provides privacy protections for California residents, giving them the right to know what personal data is collected, request the deletion of their data, and opt out of data sales. Companies operating in California must comply with CCPA provisions, which include implementing security measures to prevent breaches.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA applies to healthcare organizations in the U.S. and sets forth stringent requirements for securing patients’ personal health information (PHI). Organizations subject to HIPAA must adopt encryption, access controls, and other security measures to ensure data privacy and security.
- Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA): In the U.S., FISMA requires federal agencies and contractors to implement information security systems to safeguard government data. FISMA outlines specific cybersecurity standards and risk mitigation procedures that agencies must follow to protect sensitive information.
2. Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Standards
Failing to comply with data protection laws and regulations can have significant consequences. Organizations can face legal actions, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage from non-compliance. Here are some of the penalties businesses may encounter:
- Fines and Penalties: As mentioned earlier, non-compliance with GDPR and CCPA can lead to heavy fines. For instance, a company that fails to implement the necessary cybersecurity safeguards may face penalties for not securing personal data adequately.
- Litigation Costs: In the event of a data breach, companies may face lawsuits from affected customers, clients, or employees. Legal costs can escalate quickly, and the organization may be held liable for damages.
- Loss of Business: Failure to meet legal standards can result in loss of customer trust and damage to an organization’s reputation. Customers are increasingly concerned about how their data is protected, and companies that fail to comply with regulations may find it challenging to retain clients.
To avoid such legal consequences, businesses must regularly assess their cybersecurity policies and risk mitigation strategies to ensure they comply with applicable laws and regulations. Regular audits, legal consultations, and employee training can also help organizations stay up to date with the latest regulatory changes.
FAQs: Common Questions About Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation
In this section, we address some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to cybersecurity risk mitigation, offering detailed answers to help organizations better understand the critical aspects of protecting their digital assets.
What is the difference between risk assessment and risk mitigation?
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. It provides organizations with the information they need to understand the vulnerabilities in their systems and the most pressing threats they face.
Risk mitigation, on the other hand, refers to the actions taken to reduce the likelihood of a cyber incident or minimize the damage caused by such incidents. Risk mitigation strategies include preventive measures, incident response plans, and the implementation of security technologies to safeguard systems and data.
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies?
The effectiveness of cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies can be measured by evaluating key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Incident Frequency: A decrease in the number of security incidents and breaches is a strong indicator that mitigation strategies are working.
- Response Time: The time it takes for an organization to detect, respond to, and recover from an incident is another key measure of effectiveness.
- Compliance Status: Maintaining compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA is a sign that risk mitigation efforts are being implemented effectively.
- Vulnerability Scans: The number of vulnerabilities identified and patched over time can also be used to measure the effectiveness of risk mitigation.
What are the common cybersecurity risks businesses should be aware of?
Businesses face a range of cybersecurity risks, including:
- Phishing Attacks: Fraudulent emails designed to steal sensitive information like login credentials or financial details.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands a ransom for its release.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data who may misuse it either intentionally or unintentionally.
- Malware: Malicious software that disrupts or damages systems, steals data, or gains unauthorized access to networks.
- Data Breaches: The unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of sensitive information, often due to weak security measures.
How often should a business conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment?
It is recommended that businesses conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment at least once a year. However, this frequency should increase if there are significant changes to the organization’s infrastructure, data management practices, or if the organization undergoes a merger or acquisition. Additionally, businesses should conduct risk assessments after a major security incident or data breach to identify any vulnerabilities that may have been overlooked.
What role do employees play in cybersecurity risk mitigation?
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. They play a crucial role in mitigating risks by:
- Following Security Protocols: Employees must adhere to the organization’s cybersecurity policies, such as using strong passwords and reporting suspicious activities.
- Participating in Training: Regular employee training on recognizing phishing attempts, safe internet usage, and data protection practices is essential for reducing human error.
- Being Vigilant: Employees should be aware of potential security threats and understand how to report suspicious behavior or incidents to the appropriate team members.
By engaging employees in the organization’s cybersecurity strategy and fostering a culture of vigilance, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches.
What is the difference between risk assessment and risk mitigation?
Risk assessment is the process of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. It provides organizations with the information they need to understand the vulnerabilities in their systems and the most pressing threats they face.
Risk mitigation, on the other hand, refers to the actions taken to reduce the likelihood of a cyber incident or minimize the damage caused by such incidents. Risk mitigation strategies include preventive measures, incident response plans, and the implementation of security technologies to safeguard systems and data.
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies?
The effectiveness of cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies can be measured by evaluating key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Incident Frequency: A decrease in the number of security incidents and breaches is a strong indicator that mitigation strategies are working.
- Response Time: The time it takes for an organization to detect, respond to, and recover from an incident is another key measure of effectiveness.
- Compliance Status: Maintaining compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA is a sign that risk mitigation efforts are being implemented effectively.
- Vulnerability Scans: The number of vulnerabilities identified and patched over time can also be used to measure the effectiveness of risk mitigation.
What are the common cybersecurity risks businesses should be aware of?
Businesses face a range of cybersecurity risks, including:
- Phishing Attacks: Fraudulent emails designed to steal sensitive information like login credentials or financial details.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands a ransom for its release.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data who may misuse it either intentionally or unintentionally.
- Malware: Malicious software that disrupts or damages systems, steals data, or gains unauthorized access to networks.
- Data Breaches: The unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of sensitive information, often due to weak security measures.
How often should a business conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment?
It is recommended that businesses conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment at least once a year. However, this frequency should increase if there are significant changes to the organization’s infrastructure, data management practices, or if the organization undergoes a merger or acquisition. Additionally, businesses should conduct risk assessments after a major security incident or data breach to identify any vulnerabilities that may have been overlooked.
What role do employees play in cybersecurity risk mitigation?
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. They play a crucial role in mitigating risks by:
- Following Security Protocols: Employees must adhere to the organization’s cybersecurity policies, such as using strong passwords and reporting suspicious activities.
- Participating in Training: Regular employee training on recognizing phishing attempts, safe internet usage, and data protection practices is essential for reducing human error.
- Being Vigilant: Employees should be aware of potential security threats and understand how to report suspicious behavior or incidents to the appropriate team members.
By engaging employees in the organization’s cybersecurity strategy and fostering a culture of vigilance, businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Best Practices for Cybersecurity Risk Mitigation
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and pervasive, organizations must adopt comprehensive risk mitigation strategies to safeguard their digital assets, data, and reputation. Key actions for effective risk mitigation include identifying potential threats, conducting thorough risk assessments, adopting industry-standard cybersecurity frameworks, and implementing preventive technologies such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
In addition, understanding the legal aspects of cybersecurity risk mitigation is vital for ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. Organizations must stay informed about regulatory changes and adopt robust security measures to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
Finally, employee involvement in cybersecurity efforts is crucial for protecting the organization from insider threats and human error. Regular training, clear communication, and a proactive cybersecurity culture will help mitigate risks at every level of the organization.
Businesses can rely on trusted cybersecurity providers, like Rapid Hire Solutions, to implement best practices, conduct risk assessments, and develop effective security strategies to stay ahead of cyber threats. By adopting a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity risk mitigation, organizations can build resilience against cyberattacks and safeguard their future.
The journey toward secure systems and data is ongoing, but by prioritizing cybersecurity, businesses can protect their most valuable assets and maintain the trust of their customers.
