 Introduction to FCRA Criminal Background Check
Introduction to FCRA Criminal Background Check
In today’s competitive job market, employers face the challenging task of hiring candidates who are trustworthy, reliable, and qualified. One of the most important tools used in the hiring process is the FCRA criminal background check. But what exactly is an FCRA criminal background check, and why is it crucial for employers, particularly in the context of employment screening? In this section, we will explore the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), its role in regulating background checks, and why FCRA compliance is essential for a smooth and legally compliant hiring process.
What is an FCRA Criminal Background Check?
An FCRA criminal background check refers to a criminal history report that is conducted in compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), a U.S. federal law designed to ensure the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of consumer information used by employers, landlords, and other entities in making decisions. FCRA-compliant checks are typically used by employers during the employment screening process to assess a candidate’s criminal history and determine whether they are suitable for the job.
In essence, an FCRA criminal background check is a legally compliant method for employers to gather information on an applicant’s criminal background, ensuring they do so in a fair and transparent manner that respects the candidate’s rights.
What is the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)?
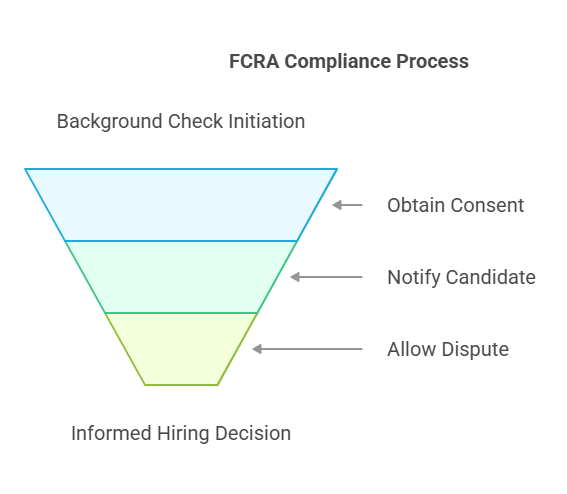
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law enacted in 1970 to regulate the collection, use, and dissemination of consumer information. Although initially focused on credit reporting, the FCRA has expanded to cover various types of consumer reports, including criminal background checks, employment records, and even medical histories.
Under the FCRA, employers who use criminal background checks for employment decisions must follow strict guidelines to ensure the accuracy of the information and the protection of applicants’ rights. These guidelines include obtaining the candidate’s consent, notifying the candidate of any negative information found, and allowing them the opportunity to dispute inaccuracies before making a hiring decision based on the report.
Why FCRA Compliance Matters
FCRA compliance is a crucial aspect of the hiring process because failure to comply with its regulations can result in serious legal consequences for employers. If an employer does not follow the proper procedures when conducting a criminal background check, they may face lawsuits, fines, or damage to their reputation. Moreover, FCRA violations could lead to candidates being wrongfully denied employment based on inaccurate or outdated criminal records.
Ensuring that criminal background checks are FCRA-compliant not only minimizes legal risks but also promotes transparency, fairness, and equal opportunity in hiring practices. It is essential for employers to understand how to conduct these checks properly to avoid any legal entanglements and maintain a positive hiring process.
The FCRA-Compliant Criminal Background Check Process
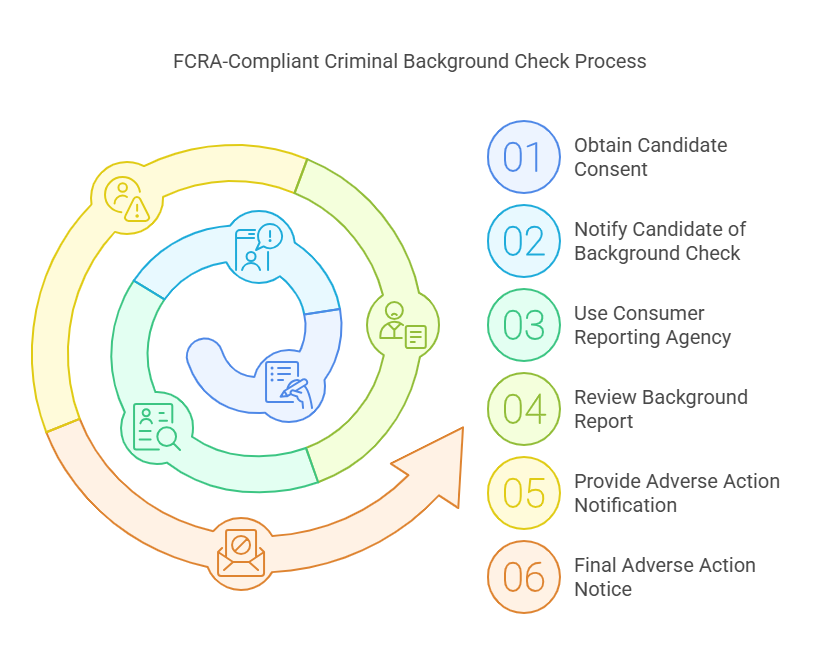
FCRA-compliant criminal background checks are not as simple as running a quick search on a candidate’s name. Instead, they follow a structured process to ensure that the employer adheres to the legal standards set by the FCRA. Here’s an overview of the steps involved in conducting an FCRA-compliant criminal background check:
- Obtain Candidate Consent: Before conducting any criminal background check, an employer must obtain written consent from the candidate. This consent should be specific and clearly state that a background check will be performed. The FCRA requires that this consent be given voluntarily, and candidates must understand that their criminal history will be reviewed.
- Notify the Candidate of the Background Check: In addition to obtaining consent, the employer must inform the candidate that they are conducting a criminal background check as part of the hiring process. This notification must be clear and transparent, ensuring that the candidate is aware of the employer’s intentions.
- Use a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA): The FCRA mandates that employers use a consumer reporting agency (CRA) or background check provider to conduct the criminal background check. These agencies gather information from various public records, including court documents, police records, and arrest histories.
- Review the Background Report: After the background check is completed, the employer must carefully review the criminal record report provided by the CRA. It is essential that the information is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to the job position being applied for.
- Provide Adverse Action Notification: If the employer decides to take an adverse action (such as not hiring the candidate) based on the criminal record, the FCRA requires the employer to follow a specific procedure. This includes sending a pre-adverse action notice that outlines the information found in the report, giving the candidate an opportunity to dispute any inaccuracies.
- Final Adverse Action Notice: If the employer decides to proceed with the adverse action after the candidate has had the opportunity to dispute the information, a final adverse action notice must be sent. This notice informs the candidate of the decision and provides details about their rights under the FCRA.
Importance of FCRA Compliance in the Hiring Process
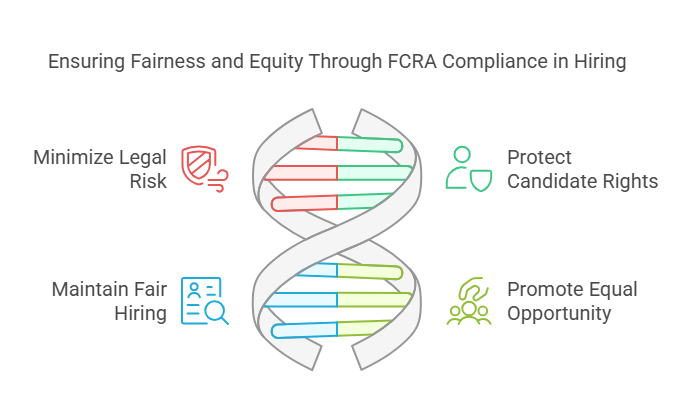
FCRA compliance is critical to avoiding legal issues in the hiring process. Here are a few reasons why FCRA-compliant criminal background checks matter:
- Minimize Legal Risk: Employers who fail to comply with FCRA regulations may be subject to legal action, including class-action lawsuits. By ensuring compliance, employers can reduce the risk of costly legal disputes.
- Protect Candidate Rights: The FCRA ensures that candidates are treated fairly during the hiring process. It provides them with the right to dispute inaccurate or outdated criminal records, preventing wrongful denials of employment.
- Maintain a Fair Hiring Process: FCRA compliance promotes fairness and transparency in hiring, ensuring that employers do not make decisions based on inaccurate or incomplete information.
- Promote Equal Opportunity: By following FCRA guidelines, employers contribute to creating an equal opportunity environment where candidates are judged based on their qualifications and abilities rather than biased or incorrect criminal records.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the FCRA during criminal background checks can lead to severe consequences for employers. If an employer neglects to follow the FCRA’s prescribed procedures, they may face lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage. Some of the potential consequences of non-compliance include:
- Legal Action: Employers may face lawsuits for violating candidates’ rights, which could result in financial penalties.
- Fines and Penalties: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) can impose fines on companies that fail to adhere to FCRA requirements.
- Negative Publicity: Employers found to be violating the FCRA may experience a loss of public trust, making it harder to attract top talent and maintain a positive reputation in the marketplace.
we discussed the importance of FCRA criminal background checks and the role of the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in regulating these checks. Now, we’ll dive deeper into the process of conducting an FCRA-compliant criminal background check, step by step. This section will outline the requirements under the FCRA, including obtaining the candidate’s consent and notifying them of any adverse actions. Additionally, we will explore best practices for conducting FCRA-compliant background checks, discuss Rapid Hire Solutions and its services, and include a comparison of criminal background check providers.
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting FCRA-Compliant Criminal Background Checks
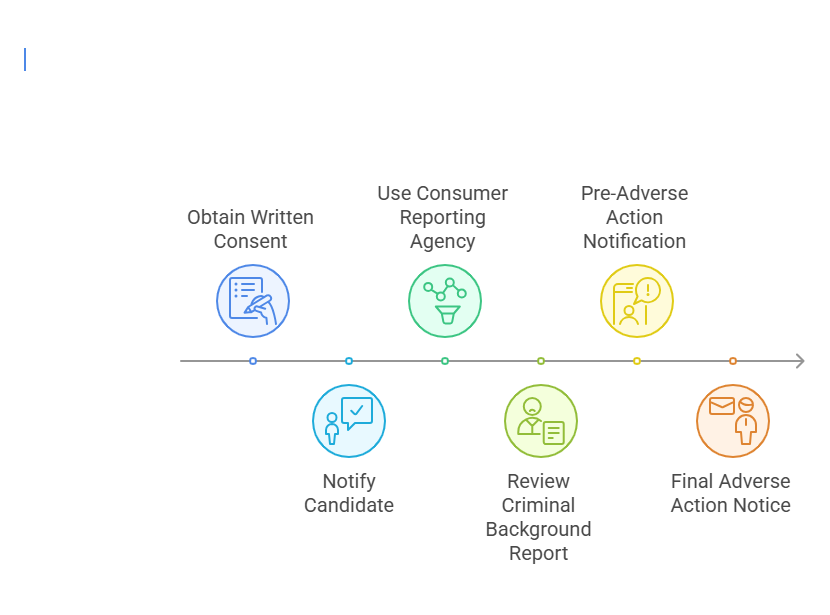
Conducting an FCRA-compliant criminal background check involves a series of important steps that ensure fairness, transparency, and legal compliance. Below is a detailed guide on how employers can conduct these checks properly:
1. Obtain Written Consent from the Candidate
Before beginning the background check process, an employer must obtain explicit, written consent from the candidate. The consent form must inform the candidate that the employer will be conducting a criminal background check as part of the hiring process. The candidate must sign this form voluntarily.
Best Practice: Make the consent form separate from the job application and keep it clear and concise. Ensure that the candidate understands what information will be gathered and how it will be used.
2. Notify the Candidate About the Background Check
Along with obtaining consent, employers are required by the FCRA to notify the candidate that a background check will be conducted. This notice should explain that the background check will include criminal records and that the information gathered will be used in making an employment decision.
Best Practice: Provide this notice before initiating the background check and retain a copy for documentation. It’s crucial to ensure that the candidate is fully informed of the process.
3. Use a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA)
The FCRA mandates that criminal background checks be performed by a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA) or a background check provider that complies with FCRA regulations. These agencies specialize in gathering criminal records and other public data, ensuring that the information is accurate and up-to-date.
Best Practice: Work with a reputable CRA that specializes in FCRA-compliant background checks. A trusted provider will ensure that the background check is comprehensive and that the information is legally obtained.
4. Review the Criminal Background Report
Once the criminal background check is completed, the CRA will provide a criminal background report detailing any convictions, arrests, or other criminal activities associated with the candidate. Employers should carefully review this report and ensure the information is accurate and relevant to the position.
Best Practice: Ensure that the criminal history is consistent with the role being applied for. Some criminal convictions may not be relevant depending on the job position or the length of time since the conviction.
5. Pre-Adverse Action Notification
If the employer is considering not hiring a candidate based on the results of the criminal background check, the FCRA requires a pre-adverse action notification. This notice must include a copy of the background report, an explanation of the candidate’s rights, and information about how they can dispute the findings.
Best Practice: Provide a reasonable period (usually 5-7 business days) for the candidate to dispute any inaccuracies before taking any adverse action. This step ensures that the candidate has the opportunity to correct any errors in the report.
6. Final Adverse Action Notice
If, after the pre-adverse action notice, the employer decides to take the final step and refuse employment based on the criminal background check, a final adverse action notice must be sent to the candidate. This notice must include the reasons for the decision and details on the candidate’s rights under the FCRA.
Best Practice: Document the process thoroughly to ensure compliance and provide transparency to the candidate. Keep records of all communications with the candidate, including the notices sent.
Best Practices for FCRA-Compliant Criminal Background Checks
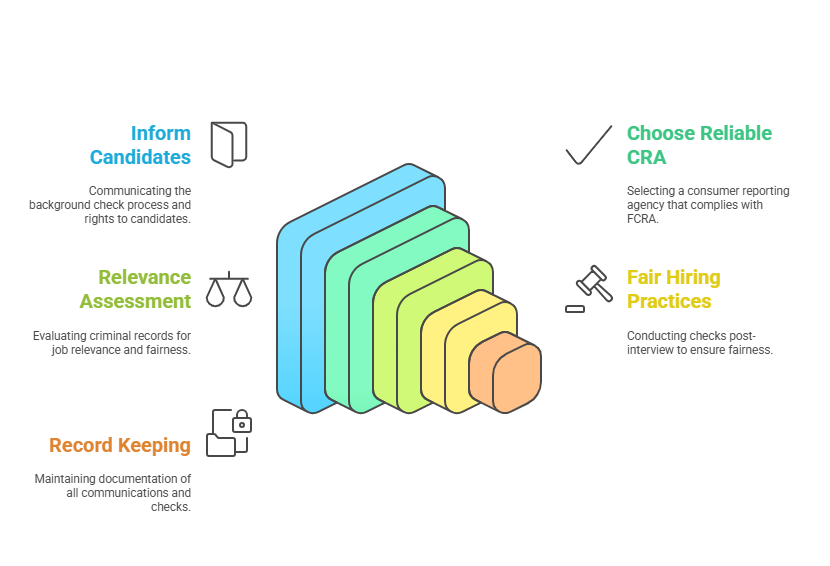
To ensure a smooth and compliant hiring process, employers should follow these best practices when conducting FCRA criminal background checks:
1. Stay Transparent and Communicative
Transparency is key in maintaining an ethical and legal hiring process. Always inform candidates about the background check and ensure they know their rights under the FCRA. This fosters trust and ensures that your organization complies with federal regulations.
2. Use a Reliable Consumer Reporting Agency
The accuracy of the criminal background report relies heavily on the CRA you choose. Select a CRA that adheres to all FCRA regulations and provides comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date information.
Best Practice: Work with an agency that offers real-time data from reliable sources and provides clear documentation on how they ensure FCRA compliance.
3. Limit Use of Criminal Records to Relevant Factors
When reviewing a candidate’s criminal history, it’s important not to make hiring decisions based solely on outdated or irrelevant convictions. The FCRA ensures that criminal background checks are used fairly and does not allow employers to use criminal history to discriminate against candidates unnecessarily.
Best Practice: Only consider criminal history that directly impacts the candidate’s ability to perform the job. For example, an applicant with a minor conviction from 10 years ago may not be a suitable basis for rejecting them for a non-sensitive role.
4. Follow Fair Hiring Practices
Comply with Ban the Box laws where applicable. These laws prohibit employers from asking about criminal history too early in the hiring process, such as during the initial job application phase. This gives candidates with criminal backgrounds a fair chance at employment.
Best Practice: Conduct criminal background checks after an initial interview or conditional job offer, as required by local and state regulations.
5. Keep Records of All Communication
FCRA compliance includes maintaining a record of your interactions with the candidate during the background check process. This documentation is crucial if your hiring decision is challenged legally.
Best Practice: Keep a complete record of the consent form, notices, and any communications related to the criminal background check in a secure location.
Rapid Hire Solutions and FCRA Criminal Background Checks
Rapid Hire Solutions is a trusted background check provider that specializes in FCRA-compliant criminal background checks. The company offers a streamlined process for employers to conduct criminal background checks while adhering to the stringent requirements of the FCRA. Some of the key services provided by Rapid Hire Solutions include:
- FCRA-Compliant Background Checks: Rapid Hire Solutions ensures that all criminal background checks comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act, protecting employers from potential legal risks.
- Fast and Reliable Reports: The company provides fast turnaround times without sacrificing accuracy, enabling employers to make informed hiring decisions.
- Data Privacy and Security: Rapid Hire Solutions takes data privacy seriously, ensuring that candidate information is securely stored and handled in compliance with applicable data protection laws.
Comparison of FCRA-Compliant Criminal Background Check Providers
| Provider | Service Features | Turnaround Time | Pricing | Additional Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Hire Solutions | FCRA-compliant checks, fast turnaround, data privacy compliance | 1-3 days | Custom pricing | Ongoing compliance updates, various background checks |
| Checkr | FCRA-compliant, real-time background checks | 1-2 days | Subscription-based | API integration for seamless hiring workflow |
| Sterling | Global background checks, FCRA-compliant | 2-4 days | Custom pricing | Drug screening, I-9 verification |
| GoodHire | FCRA-compliant, applicant-driven process | 1-3 days | Pay-per-use | Integrates with applicant tracking systems |
By following the correct steps and best practices for conducting FCRA-compliant criminal background checks, employers can make informed and legally compliant hiring decisions. This process not only ensures that employers avoid legal issues but also helps protect the rights of candidates and promotes fair hiring practices.
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion
In the final part of our comprehensive guide on FCRA criminal background checks, we will explore the legal aspects of conducting these checks, the implications of non-compliance, and the candidate’s rights under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA). Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions (FAQs) to clarify common concerns and misconceptions, and conclude with a summary of key takeaways to emphasize the importance of FCRA compliance in the hiring process.
Legal Aspects of FCRA Criminal Background Checks
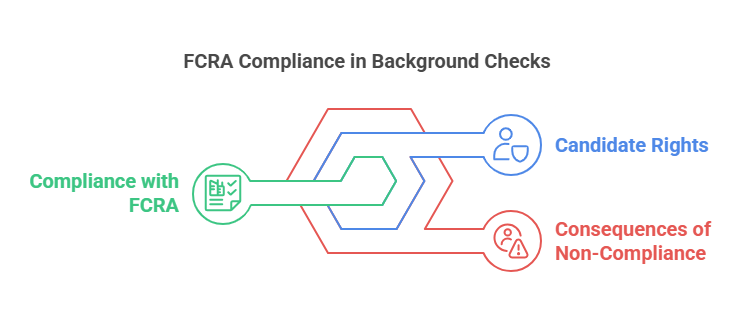
Conducting criminal background checks in compliance with the FCRA is not just a best practice—it’s a legal requirement. Employers must adhere to specific rules and regulations to ensure they are treating candidates fairly and protecting their rights. Here’s a deeper look into the legal considerations associated with FCRA criminal background checks:
Compliance with the FCRA
The FCRA outlines strict guidelines that employers must follow when conducting criminal background checks, including:
- Obtaining Written Consent: Employers must secure explicit, written consent from the candidate before conducting the background check.
- Providing Clear Notifications: Candidates must be informed about the background check process and their rights under the FCRA.
- Adverse Action Process: If the employer plans to take adverse action based on the results of the background check, they must follow a specific process, including sending pre-adverse and final adverse action notices.
Candidate Rights Under the FCRA
The FCRA grants candidates several rights to ensure they are treated fairly during the background check process:
- Right to Disclosure: Candidates have the right to know if information from their background check is used against them.
- Right to Dispute: If a candidate believes there is inaccurate or incomplete information in their background report, they have the right to dispute the findings.
- Right to a Copy of the Report: Candidates are entitled to receive a copy of their background check report, allowing them to review the information for accuracy.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with the FCRA can result in serious legal and financial consequences for employers, including:
- Lawsuits and Class Actions: Employers who fail to comply with FCRA requirements may face lawsuits from candidates who feel their rights were violated.
- Fines and Penalties: Regulatory agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) can impose fines on companies that do not adhere to FCRA guidelines.
- Reputational Damage: Negative publicity resulting from FCRA violations can damage a company’s reputation, making it difficult to attract top talent and maintain customer trust.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To further clarify the FCRA criminal background check process, here are some of the most frequently asked questions:
What is an FCRA criminal background check?
An FCRA criminal background check is a process used by employers to review a candidate's criminal history while complying with the Fair Credit Reporting Act. It involves obtaining the candidate's consent, notifying them of the process, and using a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA) to gather the relevant information.
Why is FCRA compliance important in criminal background checks?
FCRA compliance is crucial because it ensures that candidates' rights are protected and that employers avoid legal risks. Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage, while compliance promotes transparency and fairness in the hiring process.
What rights do candidates have under the FCRA?
Candidates have the right to be informed about the background check process, receive a copy of their background report, and dispute any inaccurate or incomplete information. They must also be notified if information from their report is used to make adverse employment decisions.
What should employers do if they find negative information in a candidate's background check?
If negative information is found, employers must follow the FCRA’s adverse action process. This includes sending a pre-adverse action notice, providing the candidate with a copy of the report, and giving them an opportunity to dispute the findings. If the decision to take adverse action stands, a final adverse action notice must be sent.
What are the potential consequences for employers who violate the FCRA?
Employers who violate the FCRA may face legal action, including lawsuits and class actions, as well as fines and penalties from regulatory agencies. Non-compliance can also harm the company's reputation, making it harder to attract and retain employees and customers.
Conclusion
The FCRA criminal background check is an essential component of the modern hiring process, providing employers with valuable insights into a candidate’s criminal history while ensuring compliance with federal regulations. By adhering to the FCRA’s guidelines, employers can protect themselves from legal risks, promote fairness and transparency, and make informed hiring decisions.
Understanding the legal aspects of FCRA compliance, the rights of candidates, and the importance of accurate and transparent background checks is critical for any organization looking to build a trustworthy and qualified workforce. By following best practices and leveraging the services of reputable Consumer Reporting Agencies like Rapid Hire Solutions, employers can navigate the complexities of FCRA criminal background checks with confidence, ensuring a safe, compliant, and fair hiring process.
