Understanding FCRA Background Checks: What You Need to Know
Background checks have become an essential part of the hiring process, particularly in industries where security, trust, and compliance are paramount. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) plays a significant role in regulating these checks, ensuring that both employers and applicants are treated fairly. Understanding FCRA background checks is crucial for any organization looking to protect itself from legal risks while also ensuring a smooth and efficient hiring process.
What is the FCRA?
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law enacted in 1970 to regulate the collection, dissemination, and use of consumer information, including background checks. The primary purpose of the FCRA is to promote fairness, accuracy, and privacy in the use of consumer reports, which are often used by employers to assess job applicants. In the context of background checks, the FCRA ensures that employers use this information responsibly and that job applicants’ rights are protected.
The FCRA applies not only to credit reports but also to other types of consumer reports, such as criminal records, employment history, and rental history. The law mandates that employers follow strict procedures when using these reports to make decisions about applicants, including obtaining consent and providing notification when adverse action is taken based on the information obtained.
Why FCRA Background Checks Are Important
For employers, FCRA background checks serve several important purposes. They allow companies to:
- Verify information: FCRA-compliant checks help verify the accuracy of an applicant’s credentials, employment history, and other personal details.
- Ensure safety and trust: For industries where employees handle sensitive information, money, or vulnerable individuals, background checks provide assurance that applicants do not have criminal histories or financial problems that could jeopardize the organization’s security or reputation.
- Reduce legal risks: By following FCRA guidelines, employers can mitigate the risk of lawsuits or penalties arising from improper use of background information.
For job applicants, FCRA background checks are equally important because they ensure that any information used in the hiring process is accurate and that they are treated fairly. The FCRA provides applicants with the right to:
- Dispute errors: If an applicant finds inaccuracies in their background check report, they can dispute the information with the reporting agency.
- Know when adverse action is taken: If an employer decides not to hire an applicant based on the results of a background check, they must notify the applicant and provide them with a copy of the report.
- Ensure confidentiality: The FCRA also ensures that applicants’ personal information is kept confidential and only used for employment screening purposes.
Key Requirements for FCRA-Compliant Background Checks
The FCRA imposes several key requirements on employers when conducting background checks:
- Obtaining consent: Before conducting a background check, employers must obtain written consent from the job applicant. This consent must be provided clearly and separately from other documents.
- Notification of adverse action: If an employer decides to take adverse action (such as not hiring the applicant) based on the information in the background check, they must notify the applicant. This includes providing the applicant with a copy of the report and giving them a chance to dispute any inaccuracies.
- Accuracy of information: Employers must ensure that the information used in background checks is accurate and up-to-date. If an applicant disputes any information, the employer must verify its accuracy before taking any adverse action.
- Fairness and non-discrimination: The FCRA mandates that background checks should be used in a fair manner and should not discriminate against applicants based on protected characteristics, such as race, age, or gender.
Types of Information Included in FCRA-Compliant Background Checks
FCRA-compliant background checks can include various types of information, depending on the employer’s needs and the nature of the position being applied for. Common types of information found in FCRA-compliant background checks include:
- Criminal History: Employers may request information about an applicant’s criminal record, including felonies, misdemeanors, and any convictions. The FCRA limits how far back criminal records can be considered—typically, criminal records older than seven years cannot be used in hiring decisions unless they are relevant to the position.
- Employment History: Employers may verify an applicant’s employment history, including job titles, dates of employment, and reasons for leaving. This helps to confirm the accuracy of the applicant’s resume and ensure that they have the necessary experience for the role.
- Credit Reports: For positions that involve financial responsibility, such as banking or accounting jobs, employers may request a credit report. The FCRA regulates how this information can be used and requires the employer to obtain the applicant’s written consent before reviewing the report.
- Education Verification: Employers may verify an applicant’s educational background to confirm that they hold the necessary degrees or certifications for the position.
- Motor Vehicle Records: For positions that require driving, employers may check the applicant’s driving record to ensure they have a clean driving history and are qualified to operate a company vehicle.
- Reference Checks: Employers may contact personal or professional references to verify an applicant’s character, work ethic, and qualifications.
FCRA and Consumer Rights
The FCRA provides consumers (job applicants) with several important rights during the background check process:
- Right to be informed: Applicants must be informed if a background check is being conducted.
- Right to dispute inaccuracies: If an applicant finds inaccuracies in their background check report, they have the right to dispute the information with the reporting agency.
- Right to know adverse actions: If an employer decides not to hire an applicant based on the results of a background check, the applicant must be notified and provided with a copy of the report.
The Role of FCRA in Employment Screening
The FCRA’s role in employment screening is to ensure that employers use background check information responsibly and treat applicants fairly. Employers who fail to comply with the FCRA face significant risks, including fines, lawsuits, and damage to their reputation. Additionally, applicants who feel that they have been treated unfairly or that their background check contains inaccuracies can seek legal recourse, including the possibility of suing for damages.
By following FCRA guidelines, employers not only reduce their legal risk but also ensure that they are making informed, non-discriminatory decisions that lead to better hiring outcomes.
FCRA Background Checks: Process, Compliance, and Benefits for Employers
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs the process of conducting background checks for employment purposes. As part of the broader regulatory framework, the FCRA ensures that employers use background check information responsibly, fairly, and legally. In this section, we will delve deeper into the process of conducting FCRA-compliant background checks, the benefits they offer to employers, and the compliance requirements employers must adhere to.
The Process of Conducting FCRA-Compliant Background Checks
Conducting an FCRA-compliant background check is a detailed process that requires employers to follow specific steps to ensure that applicants’ rights are protected. These steps are designed to safeguard the accuracy and fairness of the information being used in the hiring decision. Here is a breakdown of the typical process:
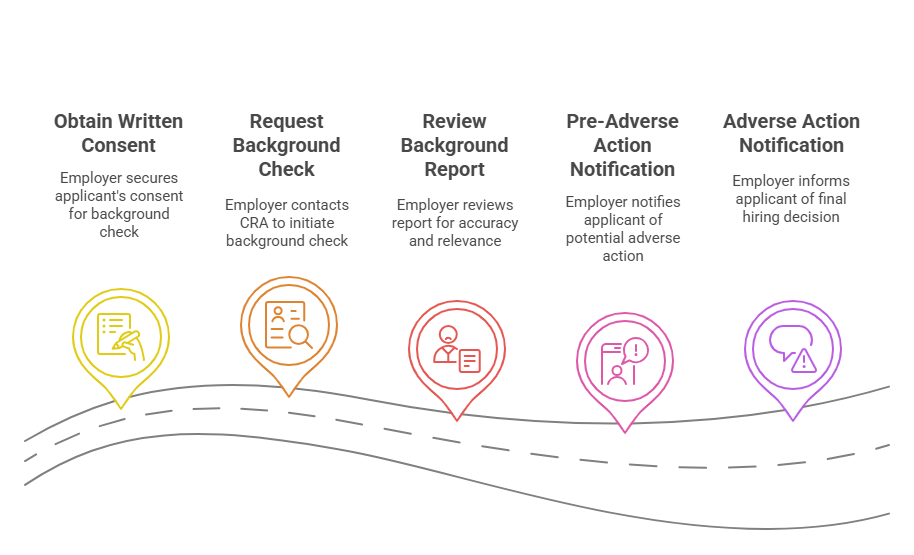
- Obtain Written Consent from the Applicant
- Before an employer can initiate a background check, they must first obtain written consent from the job applicant. This consent must be clear and separate from other documents in the hiring process. It should explicitly state that the employer will be conducting a background check, detailing what types of information will be reviewed (e.g., criminal records, credit history, employment history).
- Key Requirement: The applicant must sign a form explicitly agreeing to the background check. Failure to obtain this consent could lead to serious legal consequences.
- Request a Background Check from a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA)
- After obtaining consent, the employer can contact a Consumer Reporting Agency (CRA) to initiate the background check. A CRA is a third-party agency that collects and provides consumer information, including criminal history, credit reports, employment history, and other personal data.
- The CRA will gather the relevant information from various databases and report the findings back to the employer. It is important that the CRA complies with the FCRA’s rules, such as ensuring the accuracy of the data and maintaining confidentiality.
- Review the Background Check Report
- Once the employer receives the background check report from the CRA, they must carefully review it to assess the applicant’s qualifications. Depending on the job requirements, the employer may focus on specific aspects of the report, such as criminal records, driving records, or credit history.
- Key Consideration: Employers must make sure that they are using only accurate and relevant information in their hiring decisions. The FCRA requires that any information that could negatively impact an applicant’s chances of being hired (such as criminal convictions) must be up-to-date and accurate.
- Pre-Adverse Action Notification
- If an employer decides to take adverse action (such as not hiring the applicant) based on the background check results, they must follow the FCRA’s notification procedures. This includes providing the applicant with a pre-adverse action notice, which must:
- Inform the applicant that the decision was based on the background check.
- Include a copy of the background check report.
- Offer the applicant the opportunity to dispute any inaccurate information before the employer makes a final decision.
- If an employer decides to take adverse action (such as not hiring the applicant) based on the background check results, they must follow the FCRA’s notification procedures. This includes providing the applicant with a pre-adverse action notice, which must:
- Adverse Action Notification
- If the employer proceeds with the adverse action after giving the applicant a chance to dispute the information, they must send an adverse action notice. This notice must:
- State that the employer has made a final decision not to hire the applicant based on the background check.
- Provide contact details of the CRA that compiled the report, along with instructions on how the applicant can request a copy of the report.
- Inform the applicant of their right to dispute any inaccurate information with the CRA.
- If the employer proceeds with the adverse action after giving the applicant a chance to dispute the information, they must send an adverse action notice. This notice must:
Compliance with FCRA Regulations
Ensuring compliance with FCRA regulations is critical for employers. Non-compliance can lead to significant legal repercussions, including fines, penalties, and lawsuits. Employers must follow these key compliance requirements:
- Maintain Privacy and Confidentiality
- Employers are required to protect applicants’ privacy and ensure that background check information is used only for employment purposes. They must handle sensitive data such as criminal records and credit reports securely to prevent unauthorized access.
- Limit the Use of Certain Information
- FCRA regulations limit the use of certain types of information in background checks. For example:
- Criminal Records: Employers cannot use criminal history data older than seven years (in most cases) unless it is directly relevant to the position.
- Credit Reports: Employers can only use credit reports for positions that involve significant financial responsibilities, such as banking or accounting.
- FCRA regulations limit the use of certain types of information in background checks. For example:
- Provide Dispute Rights
- Applicants have the right to dispute any inaccuracies in their background check report. If an applicant disputes information, the employer must allow the CRA time to investigate the dispute and resolve any inaccuracies before moving forward with the hiring decision.
- Adverse Action Compliance
- Employers must strictly follow the procedures for providing pre-adverse and adverse action notices. Failing to do so could result in the applicant pursuing legal action for violating their rights under the FCRA.
Benefits of FCRA Background Checks for Employers
FCRA-compliant background checks offer a multitude of benefits for employers, including:
- Informed Hiring Decisions
- Background checks help employers make more informed hiring decisions by verifying applicants’ credentials, criminal history, and employment background. This reduces the likelihood of hiring individuals who may pose a risk to the company or its employees.
- Improved Workplace Safety
- Background checks help ensure that individuals with a history of violence, theft, or other criminal activities are not hired for roles where they could harm colleagues, customers, or the company.
- Reduced Legal Liability
- By following the FCRA’s guidelines and conducting thorough background checks, employers minimize the risk of legal action related to discrimination or improper hiring practices. Proper use of background checks also reduces the potential for negligent hiring lawsuits.
- Better Protection Against Fraud and Theft
- For positions that involve handling sensitive information or financial responsibilities, background checks can help identify applicants with a history of financial mismanagement or fraud.
- Building Trust with Customers
- Background checks demonstrate to customers that the company is committed to hiring trustworthy and responsible employees. This can enhance the organization’s reputation and build customer confidence.
Summary of FCRA Background Check Components
To provide a clearer picture, here is a table summarizing the key components of an FCRA background check and their associated legal considerations.
| Background Check Component | Information Included | Legal Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal History | Felonies, misdemeanors, arrests, convictions | Cannot include records older than 7 years (unless relevant to the job) |
| Credit Report | Credit score, payment history, debts | Can only be used for positions with financial responsibilities |
| Employment History | Previous employers, job titles, dates | Must be accurate; cannot be used to discriminate based on past jobs |
| Education Verification | Degrees, certifications, schools attended | Employers must verify the accuracy of educational claims |
| Motor Vehicle Records | Driving history, violations, license status | Relevant for positions involving driving; must be accurate and up-to-date |
Role of Rapid Hire Solutions
RapidHireSolutions plays a critical role in assisting businesses with FCRA-compliant background checks. Their services help employers navigate the complex regulations surrounding background checks, ensuring they remain compliant with state and federal laws. By leveraging their expertise, businesses can streamline the background screening process, reduce errors, and ensure they are using up-to-date, accurate information in making hiring decisions.
Rapid Hire Solutions offers various background check services tailored to meet the needs of businesses, including criminal record checks, employment verifications, credit history reports, and more. They ensure that employers adhere to FCRA requirements, making it easier for companies to protect themselves from legal risks while hiring the best candidates.